-
Posts
232 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
27
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Downloads
Gallery
Everything posted by Porter
-
Thanks for the positive feedback I used to implement a centralized queued state machine for managing each comm port. Perhaps my approach was flawed, but one reason why I stopped doing that was because I found myself having to gut existing instrument drivers to adapt them to my framework (because the VISA resource was in the handler and the logic was in the device instance). By instead forcing VISA locks to behave (as I expected), I can just wrap the existing driver with my device instance. This also allows me to develop device code that is more portable (completely independent of my application's framework).
-
Thanks ned! I hadn't come across this function yet. I'll have a look at it this weekend.
-
In particular, how can LabVIEW interface with the DefineVar function: http://beltoforion.de/article.php?a=muparser&hl=en&p=defining_variables I see that the function expects a pointer to a variable from LabVIEW. MuParser stores this pointer internally and dereferences it in the Eval function. I doubt that the value that I passed along the wire into the DefineVar function will (reliably) remain at the same memory address by the time Eval is called.
-
Has anyone taken a crack at calling MuParser or MuParserSSE from LabVIEW? http://beltoforion.de/article.php?a=muparser&p=interface
-
I'm looking forward to trying it out. I wonder how you handle forbidden combinations of: - Preallocated clone execution when there are dynamic dispatch terminals - Inline subVI into calling VI when there are dynamic dispatch terminals - Inline subVI into calling VI when there are property nodes on the block diagram - Inline subVI into calling VI with error handling - Inline subVI into calling VI with non-reentrant execution
-
Version 1.2.1 uploaded. It attempts to resolve a bug that we found in the VISA locking behavior implemented in MB_Master_Serial. See this forum topic for more information: https://lavag.org/topic/19871-visa-lock-behavior/ This version also adds a 10ms delay between retries in MB_Master_Serial "Querry.vi".
-
Just a personal preference. I am more familiar with the behavior of SEQs and the error codes that they produce. I could have used an actual semaphore though.
-
Yes. I usually forget to set the version number correctly because it such a pain to get to. I realize afterwards and have to re-build my application. Other features that I'd like to see: - Reentrancy, debugging, auto error handling settings for each VI (even if they are read-only) - For a class, it would be very useful if you could rename all of the object in/out terminals of member VIs with the click of a button
-
This is what I've come up with: VISA Lock Behavior Fixed.vi Dependency: Plasmionique Modbus Master I tested it over the weekend on one of our systems. I apologize for forcing the mb_master package on you all but the locking/unlocking code (MB_VISA_Lock.lvlib) was absorbed into it. This is what I'm doing differently: - Semaphore takes the name of the VISA resource from the Resource Name property instead of casting the session to string. - Semaphore reference is stored in the User Data property of the VISA session. Just need to keep track of 1 wire for a VISA session. - The Semaphore wraps the original VISA lock. That way we get the predictable scheduling feature of the semaphore but the safer locking features of the original VISA lock (supposedly it works over multiple LabVIEW application instances).
-
The reason why I am trying to do this is for code reuse, modularity and scalability. My system has multiple comm ports with multiple instruments on each comm port. For example, a Modbus temperature controller and a Modbus PLC can be on the same comm port. I have 2 very different labview drivers for these instruments. Their init/shutdown routines are different. The polling period is different. The data types are different. I would rather not spend the time to develop a non-reentrant wrapper to go around the read-write functions of these drivers. Besides that, what happens when I decide to move the PLC to a different comm port? I don't want to have to modify the source code and re-compile. It should just be a matter of changing a line in a config file.
-
I've implemented a workaround using names single element queues (essentially semaphores as ensegre suggested). So far it looks quite promising: My simulation code looks like this now: I will post the source code one I've completed some tests this weekend.
-
I am communicating with multiple instruments over a single serial port. These instruments are different but share a common communication protocol. Therefore, it makes sense to handle their data acquisition in separate loops. To do this, I open duplicate VISA sessions on the serial port (one for each loop). To avoid one loop interrupting the other's serial transaction, I am trying to use VISA locking: - I would expect one loop to take control of the serial port while the others wait in some sort of FIFO queue (implemented within the VISA lock primitive). - I would expect that if the timeout of the locks were set to 10 seconds, and there were 3 loops, each loop executing one serial transaction that takes less than 50ms, then the VISA lock should never timeout. In reality, this is not the case. It is actually possible that one loop can starve the others by somehow holding onto the lock over multiple iterations (See figure 1). The graphs show the amount of time (in ms) spent waiting on the VISA lock per iteration of the loop. Clearly loop 2 never has to wait while loop 1 and 3 timeout after 10 seconds. Figure 2 shows a case where the loops are not starving each other but are clearly holding on to the lock over multiple iterations before releasing it. My simulation VI is attached. COMM time is the time in ms allotted to each serial transaction. Poll period is the desired execution rate (in ms) of the loop. Starvation starts to occur when COMM time is equal to poll period. Note that I am not using "VISA Lock Async" because it is NOT re-entrant and is thus only appropriate if your system only needs to use one serial port at a time. I really didn't expect this kind of behavior. So my question is, does anyone know why VISA lock has been implemented this way? VISA Lock Behavior.vi
-
Great work! I've been using this tool for a couple of months now. I'm looking forward to trying your next release. So far I've found it most useful for editing the inheritance and localized names of my classes.
-
Thanks! My quick-drop plugins were all messed up. I had installed some unofficial plugins that took over the "Wire multiple objects together" shortcut. Successfully restored it by copying the default plugins from another machine. This shortcut will save me hours of tedious wiring.
-
Is there any way to automatically wire an index array block to a bundle by name block? Auto-wire (pressing space) just adds one wire. Note that my cluster contains data of different types so converting the cluster to an array doesn't work. If there is a quick-drop shortcut for this I would be very impressed.
-
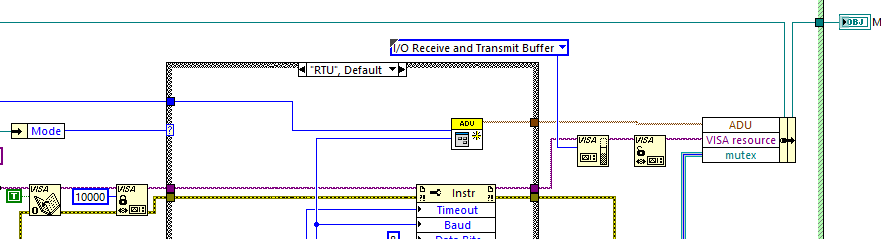
You can create a copy of the MB_ADU_RTU class and replace the Calc CRC-16 with whatever check that you want to do. You will probably also need to modify the RX ADU and TX ADU. After that, you should create a copy of MB_Master_Serial class and modify Open Serial Session to use your new MB_ADU_RTU class as its ADU. You can then use the function code vis on your new MB_Master_Serial class to communicate with your slave device. Let me know if you come up with a better way of doing this. I don't like creating copies of classes but this avoids modifying the original library.
-
Perhaps they had the intention of allowing longer length responses at some point. According to the spec, Read FIFO Queue is limited to a maximum byte count of 64. The MSB of byte count will always be zero. This is just a little annoying though since the byte count parameter for any other function code is only 1 byte long.
-
Version 1.0.5 uploaded. Does anyone know the reason why Byte Count of Read FIFO Queue (function code 24) is 2 bytes long?
-
New version uploaded (V1.0.4). Now supports function codes with responses of unpredictable length in RTU mode (other modes already supported this). In RTU mode, if the RTU_DataBytes is set to less than zero, RX_ADU.vi expects that, in the response, the byte after function code is the number of data bytes. However, if the function code is 43, Modbus encapsulated interface transport message format is assumed. For now, only MEI type 14 is properly supported. Other MEI types rely on a timeout of 200 ms to determine the end of message.
-
OK. I've worked it out. Modbus Master now has a dynamic dispatch accessor for ADU and Session Valid. I'm going to make an example for a TCP/Serial device this weekend and post an update.
-
During development I was using the RX/TX data and timestamps for debugging purposes only. I didn't really intend to expose them to the top level. I will look into creating accessors for them in the parent modbus master class. I'd rather not have the parent ADU class in the parent modbus master class though.
-
Error code -8101 means that the Slave ID of the RX message doesn't match that of the RX message. Error code -8102 means that the CRC of the RX message is invalid. I'd suggest using a different USB to serial converter. Otherwise, you could try increasing the number of retries.
-
Was it the "VISA Set I/O Buffer Size" that solved the problem?
-
The main difference that I see is that the I/O buffer sizes are set to 4096 before the first VISA write. I suspect that they are doing this because of the problem described here: http://digital.ni.com/public.nsf/allkb/60DDFED7EFEFE7188625705700750821 You can add "VISA Set I/O Buffer Size" to the "Open Serial Session.vi" of the Modbus Serial Comm Tester (located in the init case). I imagine that this would have a negative impact on performance so you should increase the timeout to 1000ms. Also it looks like they use function code 4 to read address zero. So you should try using "Read Input Registers" to read register zero.
-
Here it is for LV2012. Note that it is included with the Plasmionique Modbus Master package. You should be able to find it in LabVIEW's "examples\Plasmionique\MB Master\" directory. MB_Serial_Master Comm Tester.vi