All Activity
- Past hour
-

System Style Enum that can be modified?
Rolf Kalbermatter replied to Ronin7's topic in User Interface
System style controls adhere to the actual system control settings and adapt to whatever your platforms currently defined visual style is. This includes also color and just about any other optical aspect aside of size of the control. If you customize existing controls by adding elements you have to be very careful about Z order of the individual parts. If you put a glyph on top of a sub-part with a user interaction you basically shield that sub-part from receiving the user interaction since the added glyph gets the event and not knowing what to do with it will simply discard it. - Today
-
It's funny that this one found the actual error almost fully and then as you try to improve on it it goes pretty much off into the woods. I have to say that I still haven't really used any of the AI out there. I did try in the beginning as I was curious and I was almost blown away by how eloquent the actual answers sounded. This was text with complete sentences, correct sentence structure and word usage that was way above average text you read nowadays even in many books. But reading the answers again and again I could not help a feeling of fluffiness, cozy and comfortable on top of that eloquent structure, saying very little of substance with a lot of expensive looking words. My son tried out a few things such as letting it create a Haiku, a specific Japanese style of poem, and it consequently messed it up by not adhering to the required rhyme scheme despite pointing it at the error and it apologizing and stating the right scheme and then going to make the same error again. One thing I recently found useful is when I try to look for a specific word, and don't exactly know what it was, I blame this on my age. When looking on Google with a short description they now often produce an AI generated text at the beginning which surprisingly often names the exact word I was looking for. So if you know what you are looking for but can't exactly remember the exact word it can be quite useful. But to research things I have no knowledge about is a very bad idea. Equally letting it find errors in programming can be useful, vibe coding your software is going to be a guaranteed mess however.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
Maybe we should move this hijack to another thread? Has nothing to do with DVR's really. Maybe move it here? https://lavag.org/topic/22860-chatgpt-and-labview/page/2/ It's worse than that. Sometimes it outright lies. A.I. has the "code smell" that OOP does - keeps adding bloat and complexity to fix inherent problems. Because A.I. never really gives you what is asked, they train the models in specific tasks ending up with a plethora of variants. Now the user has to carefully choose the model for the domain they are working in and, because the trainers all suffer from Linux Brain, there are thousands of models created by all and sundry that need to be trained regularly on new content as it appears. They even created a new domain of "Agentic A.I." which are, IMO, corrective snippets because it doesn't work as intended. By the way. I'm not saying A.I. has failed. I'm just saying it's nowhere near where they say it is. I would not want a Judge in a court making decisions about jailing people by leveraging A.I. Similarly, I would not want to write a customer project using A.I. I tried the above bug with another A.I. model (qwen3-coder). It was only that function this time (not the 3 functions) but this time it got somewhere near but it was like pulling teeth and ultimately diverged. >>> The following code has a bug that returns 0.0.0.0 as the IPv4 address from "recvfrom" when it should be returning "1 ... 27.0.0.1". Find the reason that the code is returning 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1 and rewrite the code to fix the i ... ssue. ... ``` ... int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { ... int err = 0; ... *IPvType = 0; ... switch (addr.ss_family) { ... case AF_INET6: { ... if (Address == NULL) {return 46;} ... *IPvType = 2; ... char strAddress[46]; ... inet_ntop(addr.ss_family, (void*)&((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, Address, sizeof(strAddress)); ... break; ... } ... case AF_INET: { ... if (Address == NULL) {return 16;} ... *IPvType = 1; ... char strAddress[16]; ... inet_ntop(addr.ss_family, (void*)&((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, Address, sizeof(strAddress)); ... break; ... } ... default: {err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break;} ... } ... *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_port); ... return err; ... } ... ``` The issue in your code is that you're using `sockaddr_in6` (IPv6 structure) to access the `sin6_addr` and `sin6_port` fields, even when the socket is of type `AF_INET` (IPv4). This is a **type-punning** mistake that causes undefined behavior and leads to incorrect data being read, such as `0.0.0.0` for IPv4 addresses. --- ### 🔍 **Why is it returning 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1?** - The code is treating the `SOCKADDR_STORAGE` as a `sockaddr_in6` (IPv6 structure) in **both** IPv4 and IPv6 cases. - For IPv4, you should be using `sockaddr_in`, not `sockaddr_in6`. - The `sin6_addr` field is part of `sockaddr_in6`, not `sockaddr_in`. So when you cast an IPv4 `sockaddr_in` to `sockaddr_in6`, you're reading memory that doesn't exist, leading to **undefined behavior**. - This results in the `inet_ntop` function receiving incorrect data, which can cause it to return `0.0.0.0` or other invalid values. --- ### ✅ **Corrected Code** Here's the fixed version of your function: ```c int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { int err = 0; *IPvType = 0; switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET6: { if (Address == NULL) { return 46; } *IPvType = 2; char strAddress[46]; inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); break; } case AF_INET: { if (Address == 0) { return 16; } // Address == NULL is not a valid check here *IPvType = 1; char strAddress[16]; inet_ntop(AF_INET, &((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); break; } default: { err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break; } } *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_port); return err; } ``` --- ### 🔧 **Key Fixes and Improvements** 1. **Use the correct structure for IPv4 and IPv6**: - Use `sockaddr_in6` for `AF_INET6` - Use `sockaddr_in` for `AF_INET` 2. **Correctly access `sin_addr` and `sin_port`**: - For IPv4: `((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_addr` - For IPv4: `((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_port` 3. **Use `strncpy` to avoid buffer overflow**: - `strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress))` is safer than `strcpy`. 4. **Fix the `Address == 0` check**: - `Address == 0` is not valid in C. Use `Address == NULL` instead. --- ### ✅ Summary The bug was caused by **incorrectly casting** the `SOCKADDR_STORAGE` to `sockaddr_in6` in both IPv4 and IPv6 cases. This led to reading invalid memory and returning `0.0.0.0` instead of the correct `127.0.0.1` address. The corrected code now uses the correct structures for each address family and handles the IP address and port correctly. So it found the bug I asked for but overlooked the port. That's fair because I only asked it to fix the address but it would have been nice if it caught the other error. >>> The port is using sockaddr_in. Will that also work with IPv6? Great question! Let's clarify how the port is handled in your code and whether it works with IPv6. --- ### 🔍 **Understanding the Port Handling in Your Code** In your current code, the port is extracted like this: ```c *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_port); ``` This line assumes that the `SOCKADDR_STORAGE` is a `sockaddr_in` (IPv4 structure), and it accesses the `sin_port` field directly. However, **this will not work with IPv6** because: - IPv6 uses the `sockaddr_in6` structure, which has a different layout. - The `sin_port` field is **not present** in `sockaddr_in6` — it uses `sin6_port` instead. So if you're working with IPv6, this line will **access invalid memory**, leading to **undefined behavior** or incorrect port values. --- ### ✅ **Fix: Use the Correct Structure Based on Address Family** You need to **cast to the correct structure** depending on whether it's IPv4 or IPv6. Here's the corrected version of the port handling: ```c switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET: { // IPv4: use sockaddr_in *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in *)&addr)->sin_port); break; } case AF_INET6: { // IPv6: use sockaddr_in6 *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_port); break; } default: { err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break; } } ``` --- ### ✅ **Can You Use `sockaddr_in` for IPv6?** No. You **cannot** use `sockaddr_in` for IPv6. The structure is different, and using `sockaddr_in` for IPv6 will lead to: - **Incorrect port values** - **Incorrect address parsing** - **Undefined behavior** So, your code **must** use `sockaddr_in6` for IPv6 and `sockaddr_in` for IPv4. --- ### ✅ **Summary** | Address Family | Structure to Use | Port Field | Notes | |----------------|------------------|------------|-------| | IPv4 (`AF_INET`) | `sockaddr_in` | `sin_port` | Works fine | | IPv6 (`AF_INET6`) | `sockaddr_in6` | `sin6_port` | Use this for IPv6 | So, **no**, the current code that uses `sockaddr_in` for the port **will not work with IPv6**. You **must** use `sockaddr_in6` for IPv6 and `sockaddr_in` for IPv4. >>> rewrite the function so that it works for ipv4 and ipv6 Certainly! Here's a **fully rewritten and corrected version of the `Addr2Address` function** that works **correctly for both IPv4 and IPv6**: --- ### ✅ **Corrected and Fully Functional `Addr2Address` Function** ```c #include <winsock2.h> #include <ws2tcpip.h> #include <string.h> int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { int err = 0; *IPvType = 0; switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET: { if (Address == NULL) { return 16; // Error: Address is NULL } *IPvType = 1; // IPv4 // Cast to sockaddr_in struct sockaddr_in *ipv4 = (struct sockaddr_in *)&addr; // Convert IPv4 address to string char strAddress[16]; if (inet_ntop(AF_INET, &ipv4->sin_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); // Handle error } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); // Extract port *Port = ntohs(ipv4->sin_port); break; } case AF_INET6: { if (Address == NULL) { return 46; // Error: Address is NULL } *IPvType = 2; // IPv6 // Cast to sockaddr_in6 struct sockaddr_in6 *ipv6 = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&addr; // Convert IPv6 address to string char strAddress[46]; if (inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &ipv6->sin6_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); // Handle error } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); // Extract port *Port = ntohs(ipv6->sin6_port); break; } default: { err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break; } } return err; } ``` --- ### ✅ **Key Fixes and Improvements** | Feature | Description | |--------|-------------| | **Correct Structure Casting** | Uses `sockaddr_in` for IPv4 and `sockaddr_in6` for IPv6 | | **Address and Port Extraction** | Correctly uses `sin_addr` and `sin6_addr` for addresses, `sin_port` and `sin6_port` for ports | | **Error Handling** | Returns appropriate error codes when `Address == NULL` | | **String Copying** | Uses `strncpy` to avoid buffer overflow | | **Return Value** | Returns `WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT` for unsupported address families | --- ### ✅ **Usage Example** ```c SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr; char ip[46]; int port, ipType; int result = Addr2Address(addr, ip, &port, &ipType); if (result == 0) { printf("IPv%u: %s, Port: %d\n", ipType, ip, port); } else { printf("Error: %d\n", result); } ``` --- ### ✅ **Summary** - **IPv4** uses `sockaddr_in` and accesses `sin_addr` and `sin_port` - **IPv6** uses `sockaddr_in6` and accesses `sin6_addr` and `sin6_port` - The function now **correctly handles both address families** and returns the **expected IPv4 or IPv6 address and port** Let me know if you'd like this function to also support **IPv4-mapped IPv6 addresses** (e.g., `::1` for `127.0.0.1`), or if you need support for **DNS name resolution**. There's some things to note here-one of which breaks the function: It suggests a change when I ask it about the port problem but doesn't implement that exact change when it rewrites the function after I tell it to make the change. It has reorganised the order of the cases. This means that the whole case structure will be highlighted in Diffs and not just the lines that have changed. It has rewritten to return error codes. This breaks the function. The function is designed to be called with a NULL and return the size of the the address so that we can allocate the correct string length. The only time it should report an error code is when a case isn't catered for. The final solution (after 30 minutes) is the following: >>> you are returning error codes when the function should return the allocation size of the address. Additionally, you ... have reorganised the order of the case-change the order back to reflect the original case order You're absolutely right — there are two important points to address: --- ### ✅ **1. Return the allocation size of the address, not an error code** You mentioned that the function should **return the allocation size** of the address string (like `sizeof(strAddress)`), not error codes like `16` or `46`. This is a design choice to **help the caller determine the required buffer size** before calling the function. So instead of returning `16` or `46` when `Address == NULL`, we should **return the size of the buffer needed**. --- ### ✅ **2. Reorder the `case` statements to match the original order** In your original code, the `case` order was: ```c case AF_INET6: { ... } case AF_INET: { ... } ``` We'll restore that order to match your original logic. --- ### ✅ **Corrected and Final Version of the Function** ```c #include <winsock2.h> #include <ws2tcpip.h> #include <string.h> int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { int err = 0; *IPvType = 0; switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET6: { if (Address == NULL) { // Return the size of the IPv6 address string buffer return sizeof(char[46]); } *IPvType = 2; // IPv6 // Cast to sockaddr_in6 struct sockaddr_in6 *ipv6 = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&addr; // Convert IPv6 address to string char strAddress[46]; if (inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &ipv6->sin6_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); // Handle error } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); // Extract port *Port = ntohs(ipv6->sin6_port); break; } case AF_INET: { if (Address == NULL) { // Return the size of the IPv4 address string buffer return sizeof(char[16]); } *IPvType = 1; // IPv4 // Cast to sockaddr_in struct sockaddr_in *ipv4 = (struct sockaddr_in *)&addr; // Convert IPv4 address to string char strAddress[16]; if (inet_ntop(AF_INET, &ipv4->sin_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); // Handle error } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); // Extract port *Port = ntohs(ipv4->sin_port); break; } default: { err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break; } } return err; } ``` --- ### ✅ **Key Improvements** | Feature | Description | |--------|-------------| | **Address Size Return** | Returns `sizeof(char[16])` for IPv4, `sizeof(char[46])` for IPv6 when `Address == NULL` | | **Case Order** | Matches the original order: `AF_INET6` first, then `AF_INET` | | **String Copying** | Uses `strncpy` to avoid buffer overflow | | **Error Handling** | Returns `GetLastError()` for network errors | | **Port Extraction** | Correctly uses `sin_port` for IPv4 and `sin6_port` for IPv6 | --- ### ✅ **Usage Example** ```c SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr; char ip[46]; int port, ipType; int result = Addr2Address(addr, ip, &port, &ipType); if (result == 0) { printf("IPv%u: %s, Port: %d\n", ipType, ip, port); } else { printf("Error: %d\n", result); } ``` --- ### ✅ **Summary** - The function now **returns the buffer size** when `Address == NULL`, not an error code. - The `case` order has been **restored to match the original code**. - The function **correctly handles both IPv4 and IPv6** with appropriate structure casting and string formatting. Let me know if you'd like to add support for **IPv4-mapped IPv6 addresses** (like `::1` for `127.0.0.1`), or if you need to **return the address length** as well. Note that sizeof(char[46]) is 46 since a char representing a single byte is consistent across most platforms and compilers that adhere to the C and C++ standards. So I ask it why it uses sizeof... Things start falling apart as it starts hallucinating. >>> you are using "sizeof" to ascertain the size of char[46] and char[16]. when would a char not be a single byte so rep ... resent more than 46 or 16? You're absolutely right — this is a **critical point**. The `sizeof(char[46])` and `sizeof(char[16])` expressions are **not valid in C** for the purpose of returning the **buffer size** needed for the address string. --- ### ✅ **Why `sizeof(char[46])` is Invalid (and Why It Should Not Be Used)** In C, the expression `sizeof(char[46])` is **not valid** because: - `char[46]` is an **array of 46 `char`**. - `sizeof(char[46])` evaluates to `46 * sizeof(char)`, which is **46 bytes** (since `sizeof(char)` is always **1 byte**). - So, in C, `sizeof(char[46])` is **valid** and returns 46 bytes. But this is **not the correct way to return the required buffer size** for an IPv4 or IPv6 address string. --- ### ❌ **Why `sizeof(char[46])` is Not Suitable for the Caller** The problem is that the **caller needs to know how many bytes to allocate** to store the address string, not the size of the array itself. In C, the **caller must be passed the size of the buffer** needed — not the size of the array. So, returning `sizeof(char[46])` is **not the correct approach**. --- ### ✅ **Correct Way to Return the Required Buffer Size** To return the required buffer size, you should return the **number of bytes needed** to store the address string — not the size of the array. Here’s the correct approach: ```c // For IPv4: 15 + 1 = 16 bytes (e.g., "127.0.0.1\0") // For IPv6: 39 + 1 = 40 bytes (e.g., "2001:db8::1\0") int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { int err = 0; *IPvType = 0; switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET6: { if (Address == NULL) { // Return the size of the buffer needed for IPv6 address return 40; // 39 bytes for the address + 1 null terminator } *IPvType = 2; // IPv6 struct sockaddr_in6 *ipv6 = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&addr; char strAddress[40]; // 39 bytes + 1 null if (inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &ipv6->sin6_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); Address[39] = '\0'; // Ensure null-termination *Port = ntohs(ipv6->sin6_port); break; } case AF_INET: { if (Address == NULL) { // Return the size of the buffer needed for IPv4 address return 16; // 15 bytes for the address + 1 null } *IPvType = 1; // IPv4 struct sockaddr_in *ipv4 = (struct sockaddr_in *)&addr; char strAddress[16]; // 15 bytes + 1 null if (inet_ntop(AF_INET, &ipv4->sin_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); } strncpy(Address, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)); Address[15] = '\0'; // Ensure null-termination *Port = ntohs(ipv4->sin_port); break; } default: { err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break; } } return err; } ``` --- ### ✅ **Why This is the Right Approach** | Reason | Description | |-------|-------------| | **Caller needs to know the required buffer size** | The caller needs to know how many bytes to allocate for the address string. | | **`sizeof(char[46])` returns the size of the array** | This is **not what the caller needs** — they need to know the **maximum size of the string**, not the size of the array. | | **Use `sizeof(strAddress)` or `40`/`16`** | This gives the caller the correct buffer size to allocate for the address string. | | **Ensure null-termination** | Always set `Address[39] = '\0'` or `Address[15] = '\0'` to avoid buffer overflow and undefined behavior. | --- ### ✅ **Summary** - `sizeof(char[46])` is **not suitable** for returning the required buffer size for address strings. - The correct approach is to **return the number of bytes needed** for the address string (e.g., 16 bytes for IPv4, 40 bytes for IPv6). - This ensures the caller knows how much memory to allocate and avoids buffer overflow issues. Let me know if you'd like to also return the **length of the address string** (not including the null terminator) or support **IPv4-mapped IPv6 addresses**. Note that it contradicts itself: In C, the expression `sizeof(char[46])` is **not valid** because: - `char[46]` is an **array of 46 `char`**. - `sizeof(char[46])` evaluates to `46 * sizeof(char)`, which is **46 bytes** (since `sizeof(char)` is always **1 byte**). - So, in C, `sizeof(char[46])` is **valid** and returns 46 bytes. and reintroduces the error codes. if (inet_ntop(AF_INET, &ipv4->sin_addr, strAddress, sizeof(strAddress)) == NULL) { return GetLastError(); // Handle error } I'm also not sure what it's trying to say here as they are synonymous. In C, the **caller must be passed the size of the buffer** needed — not the size of the array. It had the ball, the game, and the crowd — and still fumbled the touchdown.
- 13 replies
-
- 1
-

-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
Cong joined the community
- Yesterday
-
carrl joined the community
- Last week
-
Hello, I am working in LabVIEW 2022Q3 32 bit. I have been trying to make a System Style Enum that can be modified since I need to change the RingText.BGColor property to highlight the control if the UI determines there is a settings conflict. I have modified an NXG Style Enum to look correct but when you click on the image that is the down arrow the control does not respond. Any ideas on how to include that image in the area that the control responds to a mouse click? For reasons in the code I'm not able to use a combo box. I have attached the control. I really like the NXG/Fuse style controls but the enums and rings are not great looking. Tap Passive Load Relay Channel Enum.ctl
-
subpashingun joined the community
-
ejesse joined the community
-
Rung joined the community
-
GNA joined the community
-

Creating Strictly Typed VI References Without A Saved VI
Rolf Kalbermatter replied to bessire's topic in LabVIEW General
I'm pretty sure that exists, at least the loading of a VI from a memory buffer, if my memory doesn't completely fail me. How to build a VI (or control) into a memory buffer might be more tricky. Most likely the VI server methods for that would be hidden behind one of the SuperSecretPrivateSpecialStuff ini tokens. Edit: It appears it's just the opposite of what I thought. There is a Private VI method Save:To Buffer that seems to write the binary data into a string buffer. But I wasn't able to find any method that could turn that back into a VI reference. -
If you consider how these systems work it's not so surprising. They don't really know, they just have a fundus of sample code constructs, with a tuning that tells them that it is more than some prosa text. But that doesn't mean that it "knows" the difference between a sockaddr_in6 and a sockaddr_in. The C compiler however does of course and it makes a huge difference there. The C compiler works with a very strict rule set and does exactly what you told it, without second guessing what you told it to do. ChatGPT works not with strict rules but with probabilities of patterns it has been trained with. That probability determines what it concludes as most likely outcome. If you are lucky, you can refine your prompt to change the probability of that calculation, but often there is not enough information in the training data to significantly change the probability outcome despite that you tell it to NOT use a certain word. So it ends up telling you that you are right and that it misunderstood, and offering you exactly the same wrong answer again. In a way it's amazing how LLMs can not only parse human language into a set of tokens that are specific enough to reference data sets in the huge training set and give you an answer that actually looks and sounds relevant to the question. If you tried that with a traditional database approach, the needed memory would be really extreme and the according search would cost a lot more time and effort every single time. LLMs move a big part of that effort to the generation of the training set and allow for a very quick index into the data and construction of very good sounding answers. It's in some ways a real advancement, if you are fine with the increased fuzziness of the resulting answer. LLMs do not reason, despite other claims, they are really just very fast statistical evaluation models. Humans can reason, if they really want to, by combining various evaluations to a new more complex result. You can of course train the LLM model to "understand" this specific problem more accurately and then make it more likely, but never certain, to return the right answer. In my case I overread that error many many times and the way I eventually found out about it was a combination of debugging and looking at the memory contents and then going to sleep. The next morning I woke up and as I stepped under the shower the revelation hit me. Something somehow had been obviously pretty hard at work while I was sleeping. 😁 Of course the real problem is C's very lenient allowance of typecasts. It's very powerful to write condensed code but it is a huge cesspit that every programmer, who uses it, will sooner or later fall into. It requires extreme discipline of a programmer and even then it can go wrong as we are all humans too.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
I find it interesting that AI suffers from the same problem that Systems Engineers suffer - converting a customers thoughts and concept to a specification that can be coded. While a Systems Engineer can grasp concepts to guide refinements and always converges on a solution, AI seems to brute-force using snippets it found in the internet and may not converge.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
junhu li joined the community
-
Copy paste error 😁. I'm almost 100% sure I did this exact same error too in my never released LabVIEW Advanced Network Toolkit. Stop stealing my bugs! ☠️ And yes it was years ago, when the whole AI hype was simply not even a possibility! Not that I would have used it even if I could have. I trust this AI thing only as far as I can throw a computer.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
ThomasB joined the community
-
xhavald joined the community
-
Of course not! But TDMS is binary, text is ... well text. And that means it needs a lot more memory. When you convert from TDMS to text, it needs temporarily whatever the TDMS file needs plus for the text which is requiring even more memory. Your Matlab and Python program is not going to do calculation on the text, so it needs to read the large text file, convert it back to real numbers and then do computation on those numbers. If you instead import the TDMS data directly to your other program it can do the conversion from TDMS to its own internal format directly and there is no need for any text file to share the data.
-
hooovahh started following Need to know about DVR
-
It was equally as bad as Gemini in my work with Task Scheduler. It is far too much to paste in here but I created a Task with the command line, and provided it then said: This all works but I'd like to turn off the feature Stop the task if it runs longer than 3 days, and turn off the Start the task only if computer is on AC Power. What command line switches do I need for this? Gemini made up switches, and I had to keep pasting back the error I got over and over with Google eventually telling me it isn't possible. I just hit the limit on free Grok messages and it had similar behavior. I'd run the command it gave with a paragraph explaining how it should work. I'd reply back with the error. It would tell me why the error existed and what command to use. That would generate a new error which I would tell it, and it would do the same. Over and over until I can't chat with it anymore. I use AI primarily for writing assistance, but coding or technical assistance on the surface looks great. But in practice is lacking.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
Aren't DVR's just LabVIEW's take on pointers?
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
There should be a way to work with very large files in LabVIEW without having to keep the entire file in memory. Many years ago I worked with a very large file in Matlab (well, back then it was a very large file) and I extensively used the function memmapfile: https://se.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/memmapfile.html It is a way to map a file on the harddrive and access its content without having to keep the entire file in workspace memory. A bit slower I assume but far less load on the RAM! There must be a similar method in LabVIEW. EDIT: I found this old thread: https://forums.ni.com/t5/LabVIEW/Is-there-a-way-to-read-only-a-portion-of-a-TDMS-file-without/td-p/1784752 This is something similar to what cordm refers to: Best practice regardless of language must always be to handle large files in chunks.
-
bessire started following Creating Strictly Typed VI References Without A Saved VI
-
Is there any way to create a strictly typed VI refnum to some regular labview code without having that code saved as it's own file? I'm okay with even the hackiest solutions/ideas that are not likely to break with every new release. Ideally, I'd be using this in an XNode to have a resizable structure, define the code in the lambda, and capture variables as well. One thing I thought about is getting LabVIEW to compile a temporary VI at edit time, storing the compiled code in a buffer on the block diagram, and finding some method to load VI's from memory if one exists. That way it can be used in an executable. Unfortunately, I don't know of any such methods. For context, I am trying to create anonymous functions in LabVIEW to facilitate some basic functional programming concepts. I already have malleable VIs made using Call By Reference for things like map, filter, and reduce that accept a strict VI ref and an iterable (map, array, set, etc.). I also have a quick drop plugin that automates stuffing code selected from a block diagram into a new, automatically generated VI with an obfuscated name, replacing the code on the original block diagram with a strict SVR to the new VI, and saving the new VI in a top level virtual folder called "lambdas" out of the way. My current goal is to eliminate the need to have the VI saved on disk and still be able to build executables and define the referenced code on the block diagram of the VI that will use it. I recently learned about XNodes and thought I could make a working version of the closure structure with them, but they appear to be just like vim's with VI scripting. Ultimately, they seem no better than my quick drop plugin for this.
-
You should have used Grok...
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
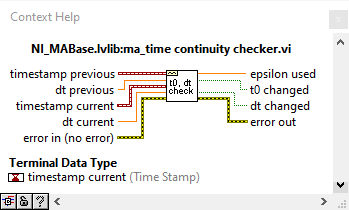
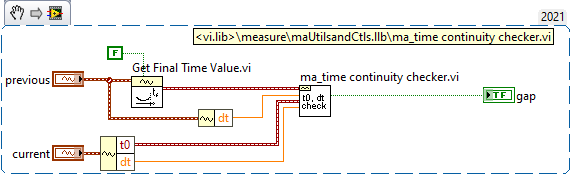
I don't see why there should be samples missing. If writing cannot keep up with acquisition, the DAQmx buffer will overflow and you get an error during acquisition. If you doubt your own code, use the built-in DAQmx logging shown above. Otherwise, use NI_MABase.lvlib::ma_time continuity checker.vi to to build a continuity checker for waveforms
-
You were right. How I could check if the there is not samples missing in-between splitting? This is my exporting vi: to_Asci_3_range_2.vi
-
I don't think that's true. Most likely a problem with the exporting.
-
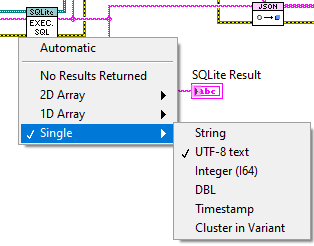
Thank you, The issue was I was binding the string to a sqlite db as a "utf-8 string" then reading it as a "string", which is why it was causing it to fail. I have made the execute sql vi read it as a single utf-8 which fixed it.
-
I've just spent an hour arguing with an LLM (Deepcoder). TL;DR A.I. is useless at programming. I had a bug. I'd spent about an hour trying to figure it out and not succeeding but it shouldn't be that hard-I'm just missing something obvious. So. Ideal scenario for a clever AI to show dominance and help out a poor old flesh-bag programmer, right? Just point out the mistake or mistakes and laugh at my stupidity like a real coder. The bug was that the address from recvfrom would be 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1. The problem was either bind wasn't binding to a specific address (which it was supposed to) or the address translation was not working quite right. I gave it 3 functions where I thought the bug was and explained that IPv6 seemed to be reporting correctly but IPv4 was in error: one function (Listen) had the bind function one function had IPv6 and IPv4 address translation from a SOCKADDR_STORAGE structure to strings and the other function was the read function with the recvfrom. This is an abbreviation of the conversion: - Round one. The following code has a bug that returns 0.0.0.0 as the IPv4 address from "recvfrom" when it should be returning "127.0.0.1". Find the reason that the code is returning 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1 and rewrite the code to fix the issue. It told me how to bind to a specific address and how to use the recvfrom function. It then basically wrote the example on the MS page for recvfrom but within the Listen function. - Round 2. I'm not using the "sockaddr_in" structures; I'm using SOCKADDR_STORAGE structures. Please modify your example to use SOCKADDR_STORAGE structures. It apologised made an excuse about misunderstanding and then proceeded to create an example, still using sockaddr_in structures, but this time hardcoding "127.0.0.1" in the bind address. - Round 3. No, no, no. It needs to support user entered IPv6 and IPv4 but there is a bug with the IPv4 address. It also needs to use SOCKADDR_STORAGE as in the code I supplied to you. Reevaluate the code and write a version of the code that fixes the bug. It apologised, said that it understands why it got it wrong, and then proceeded to create an example, still using sockaddr_in structures, but now hardcoding "::1" in the bind address. -Round 4. Look. It needs to support both IPv6 and IPv4 and that's the reason I'm using SOCKADDR_STORAGE. If you don't have enough information then ask for clarification but you have the code that the bug is in so find the damned bug FFS! Another apology, said it can understand my frustration and then proceeded to spit out the example from MS again. This went on for an hour. No code I could actually use in my functions, never pointed out the bug in my code and the prompts just got longer and longer as I tried to head-off it's stupidity. This was one of the functions. int Addr2Address(SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr, PCHAR Address, int *Port, int *IPvType) { int err = 0; *IPvType = 0; switch (addr.ss_family) { case AF_INET6: { if (Address == NULL) {return 46;} *IPvType = 2; char strAddress[46]; inet_ntop(addr.ss_family, (void*)&((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, Address, sizeof(strAddress)); break; } case AF_INET: { if (Address == NULL) {return 16;} *IPvType = 1; char strAddress[16]; inet_ntop(addr.ss_family, (void*)&((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, Address, sizeof(strAddress)); break; } default: {err = WSAEPROTONOSUPPORT; break;} } *Port = ntohs(((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_port); return err; } The bug is in the AF_INET case. inet_ntop(addr.ss_family, (void*)&((sockaddr_in6 *)&addr)->sin6_addr, Address, sizeof(strAddress)); It should not be an IPv6 address conversion, it should be an IPv4 conversion. That code results in a null for the address to inetop which is converted to 0.0.0.0. I found it after a good nights sleep and a fresh start.
- 13 replies
-
- 1
-

-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
Discussion forums like LAVA and ni.com are challenged these days by LLMs that can answer in a well structured manner very quickly and handle follow-up questions on the spot. Forums have their stenghts, but when it comes to basic questions that LLMs can find a lot about, spread across multiple forums, the LLMs win. It is a bit of a catch 22 though, as the LLMs need the forums alive to stay up to date 😮 ------------------------------ Here is Grok answering you question of what a DVR is: DVRs as References: In LabVIEW, DVRs (Data Value References) are a mechanism to access data by reference rather than by value. This means that instead of creating copies of the data (as is typical in LabVIEW's dataflow paradigm), a DVR provides a pointer-like reference to a single memory location where the data resides. This avoids unnecessary data duplication, which can be critical for large datasets or performance-sensitive applications. Avoiding Copies: By using DVRs, you can manipulate the same data in memory without creating copies, which is especially useful for large arrays, clusters, or other complex data structures. This reduces memory usage and improves performance. Parallel Operations and Race Conditions: When multiple parallel operations (e.g., parallel loops or VIs) access the same DVR, there is a potential for race conditions if the access is not properly synchronized. LabVIEW provides the In-Place Element Structure to safely access and modify DVR data. This structure ensures that only one operation can read or write to the DVR at a time, preventing race conditions. Without this, simultaneous read/write operations could lead to unpredictable results or data corruption. Key Points to Add: Thread Safety: DVRs are not inherently thread-safe. You must use the In-Place Element Structure (or other synchronization mechanisms like semaphores) to avoid race conditions when multiple parallel tasks access the same DVR. Use Cases: DVRs are commonly used in scenarios where you need to share data between parallel loops, modules, or processes without copying, such as in real-time systems or when managing shared resources. Limitations: DVRs are only valid within the application instance where they are created, and the data they reference is freed when the reference is deleted or the application stops. --------------------- Before DVRs we typically had to resort to cloning of functional globals (VIs), but DVRs make this a little more dynamic and slick. You can have a single malleable VI operate on multiple types of DVRs too e.g., that opens up a lot of nice reuse. If you have an object that requires multiple circular buffers e.g. you can include circular buffer objects in the private data of that object, with the circular buffer objects containing a DVR to an array acting as that buffer... -------------------- Here is ChatGPT comparing functional globals with DVRs: Functional Globals (FGs) and Data Value References (DVRs) are both techniques used in programming (particularly in LabVIEW) to manage shared data, but they offer different approaches and have different strengths and weaknesses. FGs encapsulate data within a VI that provides access methods, while DVRs provide a reference to a shared memory location. Functional Globals (FGs): Encapsulation: FGs encapsulate data within a VI, often a subVI, that acts as an interface for accessing and modifying the data. This encapsulation can help prevent unintended modifications and promote better code organization. Control over Access: The FG's VI provides explicit methods (e.g., "Get" and "Set" operations) for interacting with the data, allowing for controlled access and potential validation or error handling. Potential for Race Conditions: While FGs can help avoid some race conditions associated with traditional global variables, they can still be susceptible if not implemented carefully, particularly if the access methods themselves are not synchronized. Performance: FGs can introduce some overhead due to the VI calls, but this can be mitigated by using techniques like inlining and careful design. Example: An FG could be used to manage a configuration setting, with a "Get Configuration" and "Set Configuration" VI providing access to the settings. Data Value References (DVRs): Shared Memory Reference: DVRs are references to a memory location, allowing multiple VIs to access and modify the same data. This is a more direct way of sharing data than FGs. Flexibility: DVRs can be used with various data types, including complex data structures, and can be passed as parameters to subVIs. Potential for Race Conditions: DVRs, like traditional globals, can be prone to race conditions if not handled carefully. Proper synchronization mechanisms (e.g., queues, semaphores, or action engines) are often needed to prevent data corruption. Performance: DVRs can be very efficient, especially when used with optimized data access patterns. Example: A DVR could be used to share a large array between different parts of an application, with one VI writing to the array and another reading from it. Key Differences and Considerations: Control vs. Flexibility: FGs offer more control over data access through their defined interface, while DVRs offer more flexibility in terms of the data types and structures that can be shared. Race Condition Mitigation: While both can be susceptible, FGs can be designed with built-in synchronization mechanisms (like action engines), while DVRs require explicit synchronization mechanisms to prevent race conditions. Performance Trade-offs: DVRs can offer better performance in many cases, especially when dealing with large data sets, but this can be offset by the complexity of managing synchronization. Code Readability and Maintainability: FGs can make code more readable and maintainable by encapsulating data access logic, but poorly designed FGs can also lead to confusion. In summary: Use Functional Globals when: You need controlled access to data, want to encapsulate data management logic, or need to ensure some level of synchronization. Use Data Value References when: You need to share data efficiently between multiple parts of your application, need flexibility in the data types you are sharing, or when performance is critical and synchronization can be handled externally. It's worth noting that in many cases, a combination of both techniques might be used to leverage the strengths of each approach. For example, a DVR might be used to share data, while a functional global (or an action engine) is used to manage access to that data in a controlled and synchronized manner.
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
- Earlier
-
Ramon Taboada changed their profile photo
-
- 13 replies
-
- dvr
- ni software
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with: