-
Posts
5,004 -
Joined
-
Days Won
311
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Downloads
Gallery
Everything posted by ShaunR
-

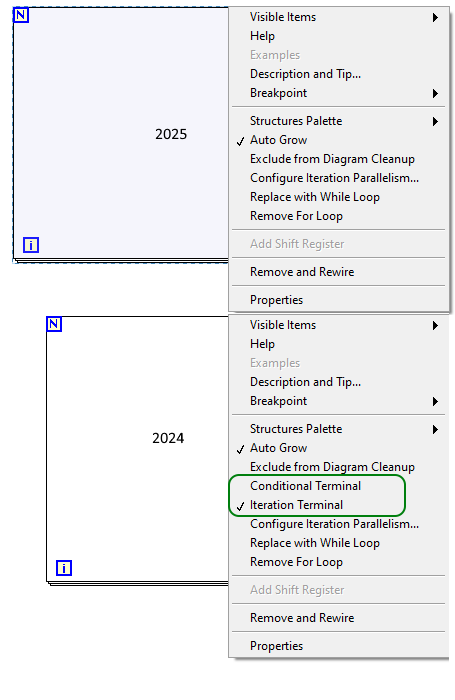
Where'd the conditional terminal go?
ShaunR replied to ShaunR's topic in Development Environment (IDE)
Makes sense. It just goes to show how ingrained workflows are and little things can trip you up. I was right-clicking over the N, over the I. Right clicking 2 pixels down/up from the edge. Top edge, bottom edge, left right. -
Probably not the feedback you are expecting but we really should do something about the nasty root loop API calls in the input API. I have somewhat progressed with this over the years and have the windows stuff all working for mouse and keyboard (and a little of the Linux) but I don't have a Mac so can't do anything on that. If there is some interest then let me know and I will see if I can allocate time to getting an API together.
-
It's not April yet so I must have missed a memo somewhere. How do I get For Loop conditional terminal back?
-
-

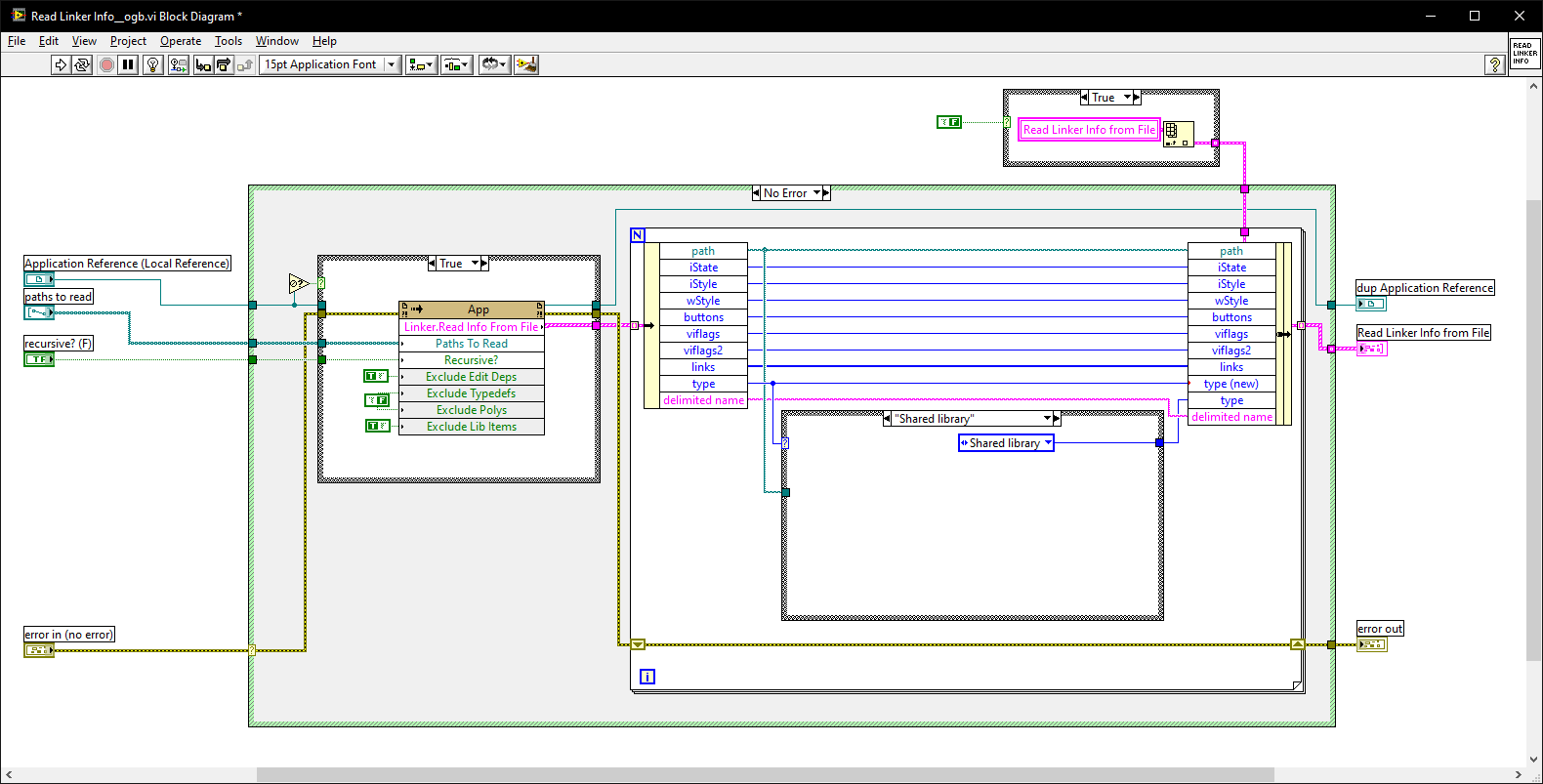
Strange VIM conversion and break down upon Source Distribution build
ShaunR replied to X___'s topic in LabVIEW General
I have similar problems now and again but it's not VIM's. Some things to try to sniff out the problem: Check project files and lvlibs with a text editor. If you have full file paths then that's a problem. File paths should be relative BUT! LabVIEW cannot always use a relative path (for example if it's on a network, different drives et.al.) Sometimes LabVIEW also gets confused but you need all paths to be relative even if it means reorganising how you structure your files. Do the above and put all dependencies in VI.lib. If you are using source control, checkout dependencies to the VI.lib directory, not your own file organisational preferences (some people like to have them on a different drive, for example). The litmus test for this is that you should be able to move your project to different locations without getting the VI searching dialogue. The search will invariably put a full path in when it finds the file-don't let it. Recursion breaks the project conflict resolution. If you have recursive functions, make sure they are not broken by manual isepction. The usual symptom is that there are no errors in the error dialogue but conflicts exist and VI's are broken somewhere. Polymorphic VI's hate recursion. If you are using polymorphic VI's recursively, don't use the polymorphic container (the thing that gives you the drop-down selector)! Only use polymorphic VI's as interfaces to other code - not itself. If you are using the polymorphic VI recursively then use the actual VI not the polymorphic container. If something gets broken you will go round in circles never getting to the broken code and multiple things will be broken. -
Nice. If you replace the OpenG VI with the above then we don't need to install all those dependencies for your demo What do you expect the cancellation behviour to be? Press escape while holding the mouse down? Mouse up cancels unless the dragged window is outside the main window? Both? Something else? I wouldn't want this feature to be a "framework" though. It would need to be much easier than that. Maybe a VI that accepts control references and it just works like above on those controls?
-
You are probably getting a permissions error on the Open (windows doesn't ordinarily allow writing "c:") which will yield a null refnum and an err 8 on the open. Your err 5000 becomes a noop as does the write. You're then clearing that error so when you come to close the null refnum it complains it's an invalid parameter - equivalent to the following. Is it expected behaviour? Yes. Should it report a different error code? Maybe.
-

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Faster execution than scripting. Scripting is incredibly slow. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Well. You could get it from the file. It's under the block diagram heap (BDHP) which is a very old structure. I personally wouldn't bother for the reasons I stated earlier but it would be much faster than using scripting. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Yes. This is exactly what is required. The User32 problem can be resolved either with file path comparison (which you stated earlier) or a list of known DLL names. I could think of a few more ways to make it automatic but I would lean to the latter as the developer could add to the list in unforeseen edge cases. The former might just break the build with no recourse. You seem to have added that for no apparent reason, from what I can tell. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
This is the same as naming a DLL x32 or x64 with extra steps. You are now adding a naming convention to a read linker and a modify linker. It's getting worse, not better. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
That doesn't help you with user32.dll. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
That is a given. The only issue I would have there is when VIPM is updated. However, you still have not explained why the "Extract Resources Info From Linker Info.vi" needs modification if all modifications can be achieved in the "Copy Resource Files and Relink VIs__ogb.vi" -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
I think it was just tongue-in-cheek whimsy. I'm still not convinced it needs fixing around there at all. As far as I can tell, it only needs to be fixed at the original VI you proffered. The only issue you seemed to have is when a binary that isn't part of the developers distribution has a 32 or 64 on it (like user32.dll). I'd be more inclined to think of your initial suggestion of comparing paths to circumvent that though. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
That may be a problem and I don't really see why it needs to be so. Is this just to resolve files that are named like user32.dll? The entry point for what you suggest seems to be here: -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Yes. This is why we have the post install VI's. There are other edge-case issues too, that cannot be resolved just by renaming. Yes. That is not a viable solution. However, what we are talking about is modifying the og libraries that VIPM uses to build (they are distributed as source), and fixing the paths BEFORE VIPM adds it to the the install so we don't need the Post Install at all. -
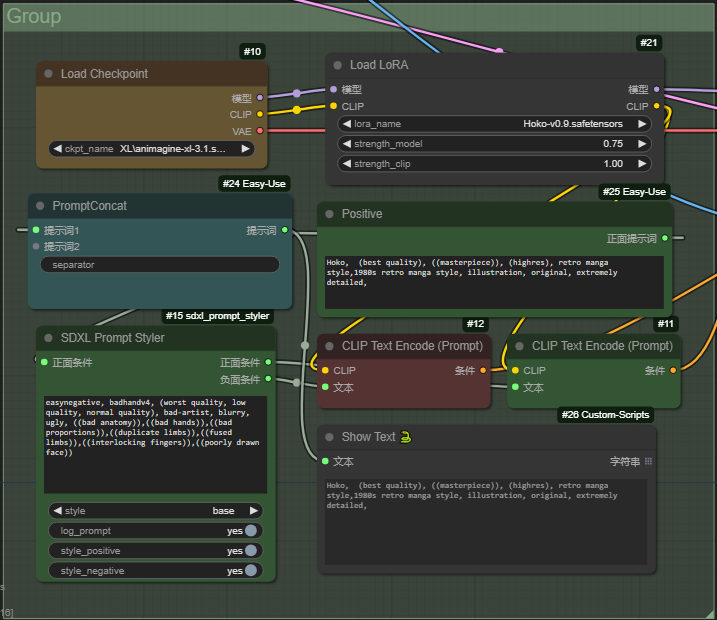
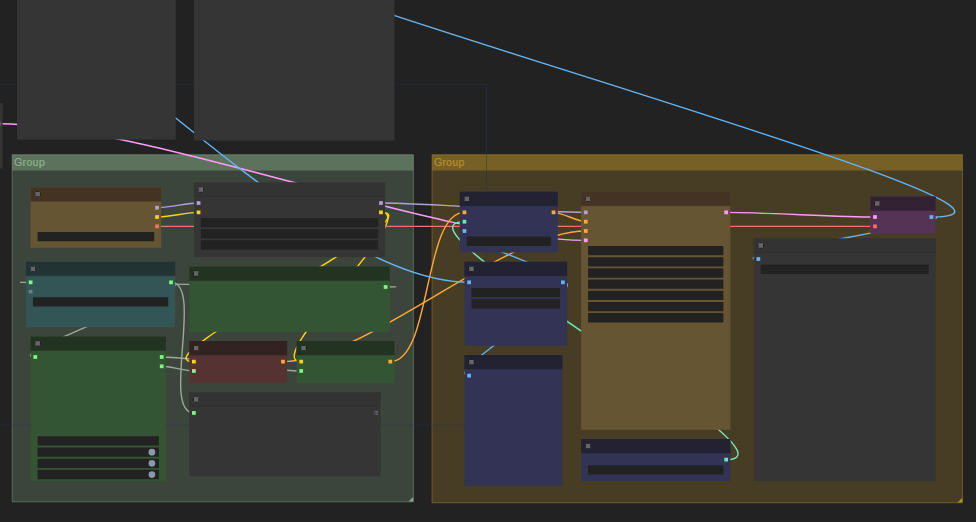
Comfy UI is a mess and I never seem to have the GB of models, extensions, clips or whatever other voodoo a workflow demands . I actually use Forge UI. That's much more manageable. Then you can add to that that the issue that all Stable Diffusion UI's have - 50 different people created their own flavour of a plugin on Github and half of them don't bother updating it anymore because they got a real job. More seriously though... With ComfyUI it is that you need to know a huge number of API's and, for want of a better description, the micro-workflows to use them. Those micro-workflows can be encapsulated just as we do a sub VI. The main criticism I have with the ComfUI is its goups. Why can't a group be represented as a control node? The groups are unrealised analogies to subVI's. Where is my "Create Node" option?
-

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
I think we are talking past each other. I don't have a problem with naming. That is just what the *.* stuff does. I'm interested in what Rolf is doing to put the *.* into the node paths. I have a problem with linking-the VI search popping up during installation, VIPM not compiling everything and asking the user to save after use. This is caused by VIPM setting in concrete, the full DLL path in the nodes when it builds and not compiling certain VI's after installation. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Both binaries can be in the same directory. No need for a Post Install or Post Uninstall. No code required to choose a 32 bit or 64 bit binary in the the different LabVIEW bitnesses. There are excellent reasons to use this nomenclature but they are thwarted by VIPM. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Not quite. I asked about your code to solve my issue. I offered what I thought was an improvement based on my requirements and, as I don't support Linux or Mac anymore, you could migrate it to the other systems if it was viable. You don't like it. Fine. It works great for me but for one edge case that you have pointed out that doesn't affect me. Assuming I cannot solve that one edge case, then I have a general Windows solution with one caveat that can go in the documentation. I'd call that progress -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
It's not a problem I have. I name them x32 and x64, if necessary, so there is no issue with the likes of user32.dll. What I do have a problem with is binaries which can be 32 or 64 bit but there is no indication in the name and the path gets "fixed" by VIPM (similar problem with TPLAT). In that scenario I want the ".*" on the end only. That is the problem it is solving and why I said I wasn't sure about the full path (I think I want just the filename). Until now I have had a similar solution to you (force changes in Post_Install and make LabVIEW search for the binaries so linking them on first load). The main difference in my solution is, perhaps, that Post_Install has the binaries in arrays on the BD and the correct bitness is saved out when installed by the user. I wanted something where I didn't update the Post_Install every time binaries changed. Perhaps we are solving different issues due to different workflows. -

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
Feel free to add them in. -
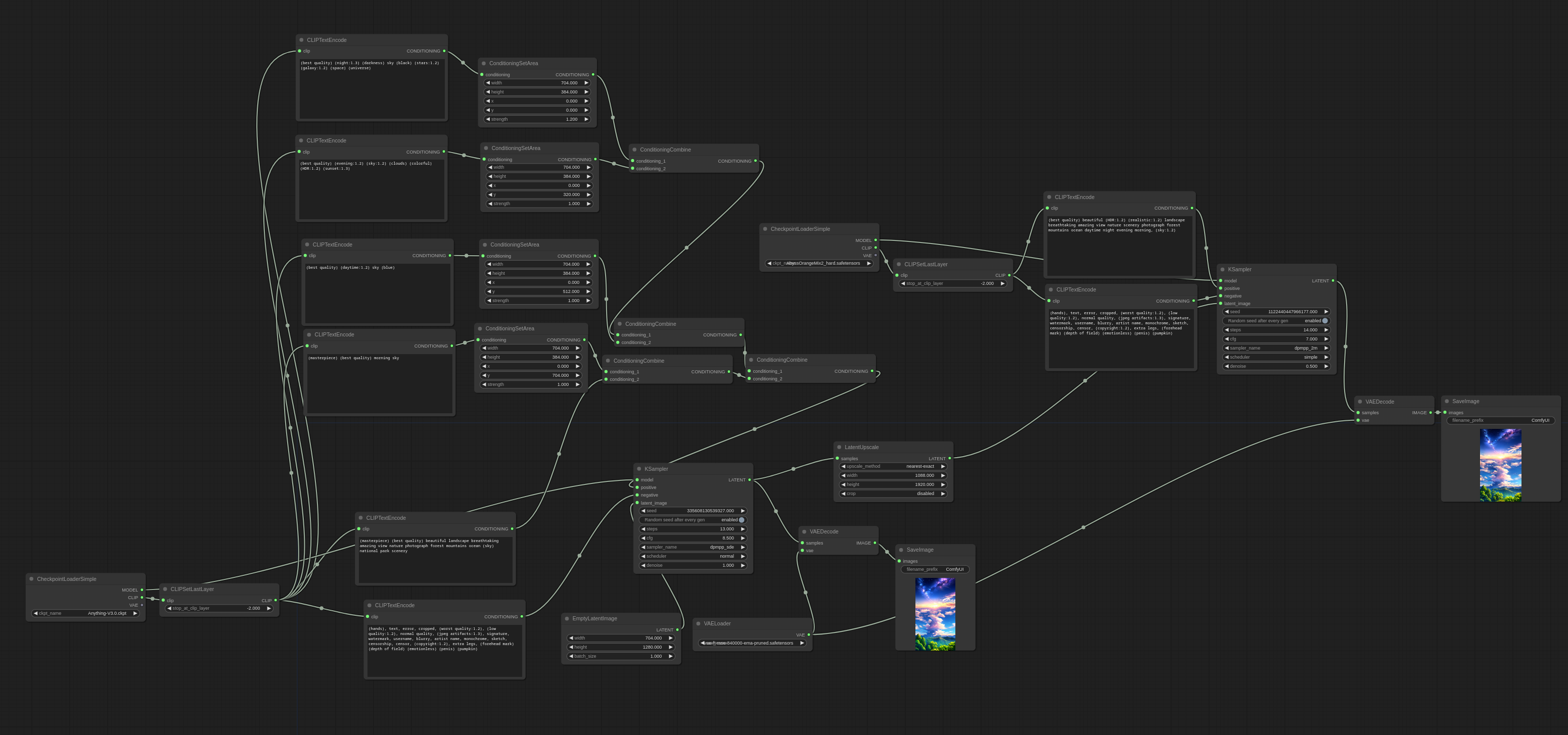
The comfyUI nodes are described by JSON in files called "Workflows" so we could import them and use scripting to create nodes. That's if we want parity. But we could support nesting which ComfUI wouldn't understand. The WebUI's are just interfaces to create REST requests which we can easily do already. I'm just trying to find a proper API specification or something that enables me to know the JSON format for the various requests. Like most of these things, there are just thousands of Github "apps" all doing something different because they use different plugins. Modern programmers can do wonderful things but it's all built on tribal knowledge which you are expected to reverse engineer. The only proper API documentation I have found so far is for the Web Services which isn't what I want - I'm running it locally.
-
I've been playing around with an A.I. Imaging software called Stable Diffusion. It's written in Python but that's not the part that interests me... There are a number of web browser user Interfaces for the Stable diffusion back-end. Forge, Automatic 1111, Comfy UI - to name a couple - but the last one, comfy UI, is graphical UI. The ComfyUI block diagram can be saved as JSON or within a PNG image. That's great. The problem is you cannot nest block diagrams. Therefore you end up with a complete spaghetti diagram and a level of complexity that is difficult to resolve. You end up with the ComfyUI equivalent of: The way we resolve the spaghetti problem is by encapsulating nodes in sub VI's to hide the complexity (composition). So. I was thinking that LabVIEW would be a better interface where VI's would be the equivalent of the ComfyUI nodes and the LabVIEW nodes would generate the JSON. Where LabVIEW would be an improvement, however, would be that we can create sub VI's and nest nodes whereas ComfyUI cannot! Further more, perhaps we may have a proper use case for express VI's instead of just being "noob nodes". Might be an interesting avenue to explore to bring LabVIEW to a wider audience and a new technology.
-

OpenG LabVIEW Zip 5.0.0-1 - stuck at the readme
ShaunR replied to PA-Paul's topic in OpenG General Discussions
I've modified your sub vi to check the actual file bitness (I think). If you target user32.dll, for example, the filename out is user32.* - which is what's expected. I need to think a bit more about what I want from the function (I may not want the full path) but it should fix the problem you highlighted (only in Windows ). Fixup Shared Library Name.vi