General
30 files
-
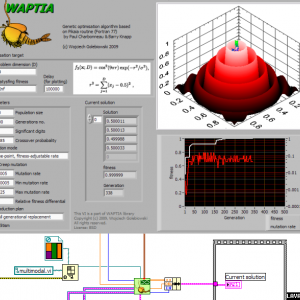
Waptia - genetic optimization algorithm
By vugie
Waptia - genetic optimization algorithm
Copyright © 2009, Wojciech Golebiowski
All rights reserved.
Author: Wojciech Golebiowski (w_golebiowski (at) tlen.pl)
Name: Waptia - genetic optimization algorithm
Type: library
LabVIEW version: 8.2
Distribution:
This code was downloaded from:
http://www.lavag.org
Description:
Waptia is general genetic optimization algorithm - it tries to maximize user supplied function of N variables (so called "Fitness Function"). Function is given as strictly typed VI reference. So the optimization goal may be described as: find such set of N numbers for which Fitness Function value is highest.
Waptia is LabVIEW implementation of quite well known genetic optimization algorithm Pikaia by Paul Charbonneau & Barry Knapp developed in Fortran-77. For more information on Pikaia and some background informatio on genetic algorithms visit: http://www.hao.ucar....kaia/pikaia.php
Pikaia name comes from lancelet-like creature which lived ages ago in Cambrian sea and waptia was another Cambrian being. Original Pikaia was developed for educational purposes, but it grew up and became widely used routine. Waptia is almost 1:1 conversion of Pikaia code (which is public domain) to LabVIEW - parts of original Fortran code are placed in related VIs - with some cosmetic modifications and improvements. Although Waptia already does real job I treat this code as starting point for further development to create sophisticated, but still easy to use genetic algorithm.
Here are Waptia's core features:
- decimal genotype encoding
- two-point crossover operator
- optional dynamically adjustable mutation rate
- optional "creep" (smoothly changing) mutation mode
- three possible reproduction plans
- elitism
- optionally stops optimization when fitness criterion is satisfied
- optimization progress may be traced on-line with notifiers
Usage is very simple - just put Waptia.vi on block diagram and provide number of independent variables and fitness function VI reference (which may be created using included template). There is of course a lot of parameters to tune, but default set usually does good job.
Installation
Preferably install VIP package with VI Package Manager
Alternatively extract ZIP to User.lib.
There are no external dependencies.
Documentation
Documentation is provided in "Waptia docs.rtf" file. It's just a description of all controls of Waptia.vi with some background information. Same information may be found in context help. Information on how to write your own fitness function is provided as comments in "Fitness Function Template.vit"
If you want to understand how Waptia works, whole code is extensively commented.
Examples
There is one quite complex example (but I hope that still understandable) located in _examples folder - "multimodal optimise.vi"
If you want any support on general or specifically genetic optimization problems, just contact me.
License (BSD):
Copyright © 2009 Wojciech Golebiowski
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3. The name of the author may not be used to endorse or promote products
derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
1,846 downloads
Updated
-
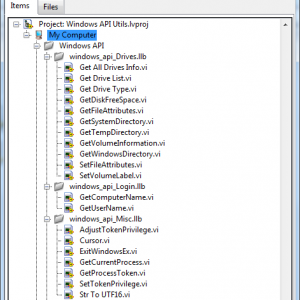
Windows API
By ShaunR
Windows API Utilities.
An eclectic set of wrapper VIs around some windows API functions.
I wrote these many years ago (1998? wow!) but have used them to some extent in virtually all my windows programs.
I've included all the original functions (accidentally re-compiled under LV 9.0) and just wrapped them up in a project and added the LAVA required stuff so your getting them "warts 'n all".
Many functions have been superseded by LabView functions and I expect many people already have their own.
But there are still some gems I couldn't do without and maybe someone will find them useful.
Installation:
Unzip to a directory of your choice.
Required Packages:
Labview 9.0 or greater
Windows XP or greater (may work on earlier versions)
Known Issues.
None.
Versioning:
Current version 1.0.
Contact: PM ShaunR on lavag.org (http://www.lavag.org)
2,119 downloads
Updated
-
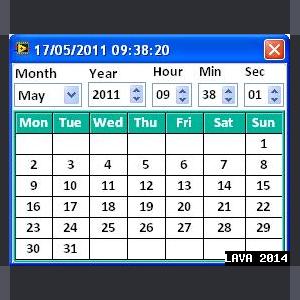
Calendar LV2009
Hi All
This Calendar is developed for the report generation.
This tool is very useful in report generation to pick up the date.
Please read readme.txt
Please give me suggestion for this to improve more.
Prabhakant Patil
4,101 downloads
Updated
-
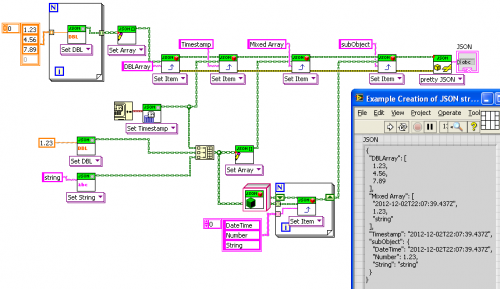
JSON LabVIEW
By drjdpowell
JSON is a data interchange format (sometimes compared to XML, but simpler). There are multiple projects to create a JSON package for LabVIEW. This is yet another one motivated by this hijacked conversation originally about a different project to convert JSON into LabVIEW Variants.
This project uses a set of LVOOP classes to match the recursive structure of JSON, rather than variants. It allows conversation to and from JSON. All functionality is available through two polymorphic VIs: Set and Get. In addition to Get and Set VIs for common data types, one can also convert directly to or from complex clusters via variant-JSON tools.
Copyright 2012-2016 James David Powell, Shaun Rumbell, Ton Plomp and James McNally.
[Note: if you are using LabVIEW 2017, please also see the JSONtext library as a an alternative.]
13,620 downloads
Updated
-
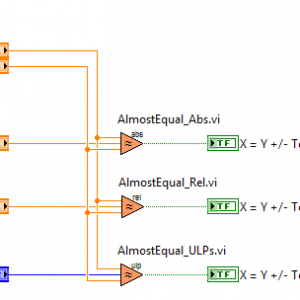
Floating Point Almost Equal
By Porter
This package contains VIs for testing equality of floating point numbers within a specified tolerance. Absolute Epsilon comparison, Relative Epsilon comparison and the ULP comparison have been implemented as described in this blog post by Bruce Dawson: http://randomascii.wordpress.com/2012/02/25/comparing-floating-point-numbers-2012-edition/ Note that the ULP comparison has not been implemented for extended precision floating point type. Installation and instructions: Install VIP package using VI Package Manager 2014. Examples: "<LabVIEW>\examples\LAVA\AlmostEqual\AlmostEqual_Example 1.vi" Demonstrates the usage of all three AlmostEqual functions. "<LabVIEW>\examples\LAVA\AlmostEqual\AlmostEqual_Example 2.vi" Demonstrates a case where exactly equal fails to produce the expected result. Development version available on GitHub: https://github.com/rfporter/FP-Equal597 downloads
- flaoting point
- equal
- (and 1 more)
Updated
-
Analog Clock_LV2010
Analog Clock_LV2010 v1.0.0
Copyright © 2012, Prabhakant Patil
All rights reserved.
Author: Prabhakant Patil
LAVA Name: Prabhakant Patil
Contact Info: Contact via PM on lavag.org
LabVIEW Versions:2010
Dependencies: Required Labview proffesional version to create XControl
Description: This is simple try to create analog clock.
Version History: v1.0.0: Initial release of the code.
License: BSD
Distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 (http://creativecommo.../about/licenses)
See link for a full description of the license.
Support:
If you have any problems with this code or want to suggest features:
please go to lavag.org and Navigate to LAVA > Resources > Code Repository (Certified) and
search for the "Analog Clock_LV2010" support page.
Distribution:
This code was downloaded from the LAVA Code Repository found at lavag.org
1,515 downloads
Updated
-
Convert between ASCII and Unicode
By crelf
Copyright © 2006, Christopher G. Relf
All rights reserved.
Author:
Christopher G. Relf
christopher_relf@yahoo.com
Distribution:
This code was downloaded from:
http://forums.lavag....odule=downloads
Description::
Convert between ASCII and Unicode
Version History:
1.1.0: Faster ASCII to UNicode alogrithm
1.0.1: Bug Fix - Removed increment in "Convert Unicode to ASCII.vi"
1.0.0: Initial release of the code.
2,539 downloads
Updated
-
Random permutation
By syrus
Copyright © 2006, 2007, Syrus Nemat-Nasser
All rights reserved.
Author:
Syrus Nemat-Nasser
**see readme text for email address**
Description::
This SubVI takes a positive I32 integer n as input and generates a uniformly random array of the integers from 0 to n-1 as output. It is equivalent in function to the ‘randperm’ command in MATLAB. If a non-positive value is provided, an error is raised to alert the caller.
Version History:
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
1.1.0:
Added input validation, error handling, and the option to use "MATLAB mode" and generate a permutation of the integers from 1 to n instead of 0 to n-1, where n is the value wired to the size input. Added a "convert to I32" before feeding the random index to the array functions to eliminate two coercion dots. Updated description to reflect these changes. Changed wiring pattern to 4-2-2-4 and changed icon to accomodate additional terminals.
2.0.0:
Added a random seed input to allow the user to optionally seed the random number generator to produce a specific random permutation. The VI now uses the Uniform White Noise PtByPt function which is not available in the LabVIEW Base package. Users who have the Base package may need to use version 1.1.0 which is still included in the distribution.
994 downloads
Updated
-
VI_path_listing
By torekp
VI_path_listing V1.0.0
Copyright © 2006, Huron Valley Steel Corporation
All rights reserved.
Author:
Paul Torek
contact through http://forums.lavag.org, by sending PM (private message) to torekp
Description:
Lists the paths of all VIs in memory other than itself, with the (optional) exception of vi.lib VIs. Note that if you do not exclude vi.lib, some of this VI's subVIs will appear on the list. Prompts user to save the list to a text file or to Cancel the save operation.
This VI might be useful to those who do not use a rigorous source code control scheme, but still want to keep track of many VIs.
Version History:
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
493 downloads
Updated
-
Windows Environment Variable Reader Writer
By hooovahh
Windows Environment Variable Reader Writer Vc
Copyright © 2006, Brian Hoover
All rights reserved.
Author:
Brian Hoover
**see email address in readme txt**
Description::
Purpose:
This Vi was made so that you can easily view and create environment variables from within Windows XP.
Features:
You are able to read all environment variables which you have available to you at the command prompt by typing "set". It also can write environment variables by writing them to the registry in the following location:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
Also for added safty it will check the name you are trying to use, and won't allow its creation if a variable with that name already exists.
Usage:
To use this VI you need to be using Labview version 8.20. With Labview 8.20 installed open the VariableReadWrite.vi file, then click run. While it's running open the View Variables tab and click "Refresh Variables" to view all your command prompt variables.
Two String arrays are created, the Name of the variables, and their values. A text window is also displaying what the user would see if they typed "set" at a command prompt.
To create a variable open the Create Variables tab and fill in the information for Variable Name and Variable Value; then click Create Variable. Please note that you may need to log off then back on for the new variable to take effect.
If needed there is a "Run Regedit" button which will open the registry. From here you can see the newly created variables in the location mentioned in the Features section.
When you are done click stop to end the program.
Version History:
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
1,483 downloads
Submitted
-
log event error
This VI logs an Application event associated with "error" to the Windows Event Viewer (eventvwr.exe). An event description includes the "error" source and code along with the leading "reason". This information can be viewed by opening an Event Properties window in the Event Viewer.
734 downloads
Updated
-
Game of Life
By eaolson
Author:
Eric Olson
--see readme file for email address
Description:
Conway's Game of Life is a fun little simulation of a group of cells. How new cells are born and how old cells die is decided by a simple set of rules, but can lead to complicated behavior by the entire colony. I've always found this simulation to be interesting and I thought coding it in LabVIEW would be a fun exercise. Comments and critiques of either the game or of my coding style are always welcome.
The basic rules are simple:
1. A cell that has one or zero neighbors dies of lonliness.
2. A cell that has four or more neighbors dies of overcrowding.
3. An empty cell that has exactly three neighbors containes a new cell in the following generation.
A thorough explanation of the Game can be found at http://web.archive.o...7s_game_of_life .
Dependancies:
This uses the OpenG time, file, and variantconfig libraries. They are not included.
Download them via the OpenG Package Manager: http://web.archive.o...p?showtopic=233
Change Log:
1.0.0: Initial release of the code.
1.0.1: Include readme.txt in the zip file.
1.1.0: Added Open and Save As functions (in the menubar). Added an About dialog. Removed the Exit button (redundant to Close).
1.1.1: Forgot to include the .rtm file in the distribution. Rows/columns now update when opening a .gol file.
1,268 downloads
Updated
-
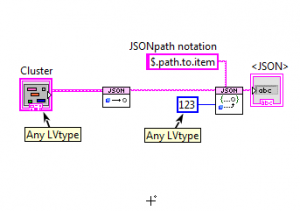
JSONtext
By drjdpowell
Package for working with JSON. Uses high-speed text parsing, rather than building an intermediate representation as with prior LabVIEW JSON libraries (this is much faster). Allows easy working with "subitems" in JSON format, or one can convert to/from LabVIEW types. Uses the new "malleable VIs" of LabVIEW 2017 to convert to any LabVIEW type directly.
JSON text makes use of a form a JSON Path notation, allowing easy and rapid access to the subitems of interest.
Requires LabVIEW 2017 and install by VIPM 2017 or later.
Original conversation about JSONtext.
On the LabVIEW Tools Network.
JDP Science Tools group on NI.com.
Copyright 2017 JDP Science Limited
1,064 downloads
Updated
-
LV muParser
By Porter
LV-muParser provides a simple LabVIEW API for muParser fast math expression parser.
A modified version of muParser v2.3.5 is included.
You will find the muParser API in the functions palette under "Addons > LAVA > muParser"
muParser: https://beltoforion.de/en/muparser/
LV-muParser source on github: https://github.com/rfporter/LV-muParser
This package has been tested on Windows 10 & 11 and Ubuntu Linux 20.04.
Documentation here: https://github.com/rfporter/LV-muParser/blob/c413686832caaff8179de923b388e21f9ca09161/Docs/LV-muParser User Guide.pdf
410 downloads
Updated
-
Fourier Epicycles
This VI program implements the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to draw any drawn shape outline with epicycles as demonstrated in this video.
For more information on the mathematical principles, please watch this video by Mathologer.
How to Use:
1.Unzip the attached zip file.
2.Open Main.vi file.
3.Run the VI.
4.Draw a shape.
4.Enjoy animation!
105 downloads
Updated
-
Y Controls Support - Version 2.0.2.0 Installer.zip
Installs support for Y Controls. Requires LabVIEW 2019 or later.
133 downloads
Submitted
-
BlueSerialization
By bjustice
Serialize and deserialize LabVIEW classes using either JSONtext or TOML
Official documentation: https://github.com/justiceb/BlueSerialization
13 downloads
Submitted
-
game TIC-TAC-TOE Game
By leumaseoj
Tic Tac Toe is a fun kids game. It created it back in 2011 when I was interning and learning LabVIEW. Please feel free to download and play this game.
TIC-TAC-TOE.zip
54 downloads
Submitted
-
Array Point to RowCol
By JDave
Copyright © 2006, dsaunders
All rights reserved.
Author:
dsaunders
--see readme file for contact information
Description:
Converts a pixel coordinate to an array index. Returns an array of indices with a length equal to the number of array dimensions. Also returns if the point is within the content rectangle (not on the caption, scrollbars, etc.)
Works on any N-dimensional array regardless of visibility of caption, label, index display, or scrollbars. Designed to be used on mouse events that provide the mouse coordinates.
Limitations: Property nodes do not indicate the array border width, nor if the user has chosen to display an element gap. These inputs are thus provided on the VI.
Version History:
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
1,473 downloads
Submitted
-
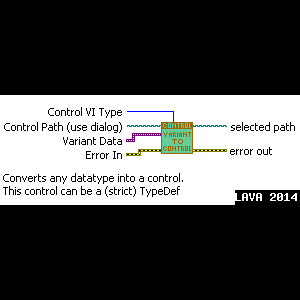
Variant to Control
By Ton Plomp
opyright © 2007, Ton Plomp
All rights reserved.
Author:
Ton Plomp
--see readme file for contact information
Description::
This tool converts any datatype into a control, this control can be typedef, a special Use-case VI is added:
Array of strings to an enum.
Especial usefull if a list of allowed values is avialable and is case sensitive (XML...)
The control can be saved as a typedef
Originated from Array To Enum
Acknowledgements:
Uses code by Bob Billier from his RTM to Enum tool
Dependencies:
Uses the following OpenG toolkits:
oglib_lvdata-2.7-1
oglib_error-2.3-1
oglib_file-2.8-1
These can be installed with VIPM (http://jkisoft.com/VIPM)
Version History:
1.1.0:
Added Variant to control
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
2,272 downloads
Updated
-
Self-Decimating Storage VIs
By torekp
Copyright © 2007, Huron Valley Steel Corporation
All rights reserved.
Author:
Paul Torek
--see readme file for contact information
Description:
These files allow the programmer to maintain a fixed-sized representative sample of data, regardless of how many data sets are accumulated. The storage may be in the form of a shift register (a.k.a. VI Global) - VIG_self_decimating.vi performs this job - or in the form of a binary file on disk - VIG_decimation_indices.vi and write_2Ddbl_decim8_REentrant.vi do that job, with help from decimatd_evenly_spaced_2D_DBL.vi and decimated_cleanup_2D_DBL.vi. Note that the given VIs are intended for storing 2D DBL arrays, but it is straightforward to modify them to do other formats such as 1D i32 arrays.
Labview 8.0
Version History:
1.0.0:
Initial release of the code.
526 downloads
Submitted
-
Strings Levenshtein Distance
Copyright © 2008, Leif S. Kirschenbaum
All rights reserved.
Author:
Leif S. Kirschenbaum
--see readme file for contact informaation.
Description:
This VI computes the Leventshein distance between two strings.
It is based on the pseudocode found in Wikipedia online:
http://en.wikipedia....shtein_distance
"The Levenshtein distance between two strings is given by the minimum number of
operations needed to transform one string into the other, where an operation is an
insertion, deletion, or substitution of a single character."
It functions by creating a step matrix which is N+1 x M+1, where N and M are the
lengths of the two strings to be compared, and filling in each cell of this matrix
indicating how many steps (insertions, deletions, character substitutions) are required.
The total number of steps to convert one string into the other is given by the last cell
in the matrix.
Change Log:
1.0.0: Initial release of the code.
629 downloads
Updated
-
Railroad Interlocking Controller
Copyright © 2009, Oliver Barrett
All rights reserved.
Author:
Oliver Barrett
--see readme file for contact information
www.linkedin.com/in/orbarrett
Description:
THE APPLICATION CONTROLS A SIMULATED RAILROAD INTERLOCKING CONSISTING OF PASSENGER STATION TRACKS, A GRADE CROSSING BETWEEN TWO RAILROADS AND A RAILROAD SWING BRIDGE.
All switches and track signals are controlled for the purpose of safely lining one train movement through interlocking at a time. Simulated occupancy of each track section by a train movement is displayed.
Interlocking operator can select the following functions from the application screen:
1. Line a selected track switch for movement into or out of the passenger station siding tracks.
2. Line one of five preconfigured interlocking configurations (eastbound, westbound, northbound, southbound or Stop), in preparation for a simulated movement in the same direction (movement will wait outside interlocking limits if configuration at Stop).
3. Select a movement direction and initiate a simulated train movement through interlocking.
A simulated movement (begun by clicking on the Initiate button) will not proceed completely through the interlocking unless the latter is configured for the same direction as the direction of movement. Such a movement may progress partway until it encounters a red signal and will then stop. It may be restarted by first lining the interlocking for the proper direction and then clicking on Initiate again.
Track signal indications will update in real-time to reflect occupancy condition (unless overriden by current interlocking configuration). The indicator for an occupied track section appears orange, otherwise green.
Each signal indicates PROCEED (green) or STOP (red). One or more signals will be forced to display STOP as part of a preconfigured interlocking movement direction (irrespective of track occupancy).
LABVIEW STRUCTURE
The application uses a Producer-Consumer (Events) design pattern. The interlocking function requests are handled by the producer loop, with separate consumer loops for lining a siding switch, configuring an interlocking direction and initiating a simulated train movement. A separate display loop executes in parallel.
Separate queues are used to pass operator requests for lining a track switch, configuring an interlocking direction and selecting a direction for simulated train movement, using a different enum typedef for each. State machine design patterns are used within the track switch lining, interlocking configuration and interlocking movement subVIs.
Four functional global variables are used for all state data involving track occupancy, switch and bridge states, signal override states (the latter used for lining a given interlocking direction) and current relative movement location/movement direction.
The display loop is initialized by a notifier at the beginning of application execution and runs in parallel to continuously update track occupancy display along with switch and bridge states and all signal indications reflecting interlocking conditions.
SubVIs are used in the display loop to read the binary state word supplied by the functional global variables associated with the track occupancy states, switch/bridge position states and signal override states.
Dependencies:
None.
Change Log:
1.0.0: Initial release of the code.
1,172 downloads
Submitted
-
SAPI TTS(Text To Speach) Library
By syrus
Copyright © 2007, Syrus Nemat-Nasser
All rights reserved.
Author:
Syrus Nemat-Nasser
--see readme file for contact information
Description::
A simple set of Sub-VIs to efficiently implement text-to-speech in LabVIEW applications on Windows using the Microsoft Speech API (SAPI).
Version History:
1.1.0:
Updated SAPI Speak SubVI: SAPI Speak is now polymorphic, accepting either a text string or a file path (which should point to a text file containing text to speak). In addition, SAPI Speak now handles speech flags correctly thanks to code contributed by LAVA user 'jdunham' included in this release.
1.0.0:
Initial release.
1,443 downloads
Submitted
-
Watermark hidden in text string
By JohnS
This software is made to hide watermark text inside your text without changing the text content
The watermark is buried in the space characters of your text !
It is "not" possible to find the watermark in the text only if you know where to look.
You can make sure that text you have written is not manipulated by somebody without breaking the watermark....
How things work you can see in the attached example_watermark file.
The file Spacy_watermark.vi is the packer and recovery of the watermark text inside a text string.
Copy the watermarked text inside a document (.doc, .txt, .html) so this text is tagged with your watermark of choice.
Explore how its done...... and let me know if you like it !
John
1,151 downloads
Updated